Poor inventory management costs businesses up to 35% in unnecessary holding expenses.
Stockouts lead to lost sales, while excess inventory ties up capital that could fuel growth.
That’s why modern warehouses face mounting pressure to optimize operations, reduce errors, and meet customer demands faster than ever.
These 11 proven warehouse inventory management tips will help you improve accuracy, reduce costs, and streamline operations in 2026.
11 Warehouse Inventory Management Tips
1. Implement Regular Cycle Counting
Cycle counting involves auditing small portions of your inventory continuously throughout the year, rather than conducting a single annual physical count. This approach maintains accuracy without disrupting operations.
Organizations that use cycle counting achieve over 95% inventory accuracy, compared to 80%with annual physical counts alone. The method allows you to identify and correct discrepancies quickly before they compound into larger problems.
Here’s how to implement cycle counting:
- Classify inventory using ABC analysis (A items = high-value, counted quarterly; B items = medium-value, counted biannually; C items = low-value, counted annually).
- Schedule daily counts for specific sections or categories.
- Use the first or last hour of shifts when activity is lower.
- Assign counts to staff who don't have a stake in the accuracy of numbers.
- Leverage barcode scanners or RFID technology to speed up counting and reduce human error.
Human error remains the leading cause of inventory inaccuracies in warehouses worldwide, according to multiple industry studies, including Zebra Technologies’ Warehousing Vision Report, resulting in costly mispicks and inaccurate counts. Cycle counting with automated technology helps minimize these errors.
2. Adopt the Right Inventory Management Method (FIFO, LIFO, or FEFO)
Choosing the correct inventory flow method prevents product obsolescence, reduces waste, and ensures optimal stock rotation.
FIFO (First In, First Out): The oldest inventory is sold or used first. This method is essential for perishable goods, food products, pharmaceuticals, and items susceptible to obsolescence. Approximately 55% of companies use FIFO as their primary inventory method because it aligns with natural consumption patterns and prevents waste.
LIFO (Last In, First Out): The newest inventory is used first. This method works for non-perishable items such as building materials, raw materials, or products with long shelf lives, where storage time doesn't affect quality. However, this method is not permitted under IFRS (Financial Reporting Standards) for inventory valuation in financial reporting.
FEFO (First Expired, First Out): Items with the earliest expiration dates are shipped first, regardless of when they arrived. This method is critical for health-related, pharmaceutical, and any products where expiry dates take precedence over arrival dates.
When implementing these methods, consider the following:
- Use flow racks or gravity-fed systems for FIFO compliance.
- Implement push-back racking systems for LIFO operations.
- Label all inventory with precise dates (received date and expiration date).
- Configure your WMS to suggest picks based on your chosen method automatically.
- Never mix products with different expiration dates in the same bin.
3. Leverage Warehouse Management System (WMS) Technology
The global warehouse management system market reached $2.88 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 19.9% CAGR through 2030. This growth reflects WMS's critical role in modern operations.
A WMS automates inventory tracking, optimizes pick paths, manages multiple warehouse locations, and provides real-time visibility into stock levels. Over 90% of businesses will automate processes using WMS by the end of 2025.
Key benefits of WMS include:
- Real-time inventory tracking. Know exactly what you have, where it is, and when it arrived.
- Automated replenishment alerts. Prevent stockouts with advance notifications.
- Optimized pick paths. Reduce travel time and increase fulfillment speed.
- Integration capabilities. Connect with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), accounting, and order management systems.
- Data analytics. Generate reports on inventory turnover, velocity, and warehouse performance.
Cloud-based WMS solutions have become the preferred deployment method, offering lower upfront costs, automatic updates, and scalability. Businesses with optimized supply chains have 15% lower supply chain costs and three times faster cash-to-cash cycles.
4. Optimize Warehouse Layout and Organization
Strategic warehouse design reduces travel time, minimizes picking errors, and increases throughput. Your layout should facilitate efficient product flow from receiving to shipping.
Consider the following layout optimization strategies:
- Zone high-velocity items. Place fast-moving products closest to shipping areas to reduce pick time.
- Create dedicated zones. Separate receiving, storage, picking, packing, and shipping areas.
- Implement vertical storage. Maximize cube utilization by storing up, not just out.
- Establish clear pathways. Wide, well-marked aisles prevent congestion and accidents.
- Use slotting optimization. Regularly analyze pick data and reposition products based on velocity.
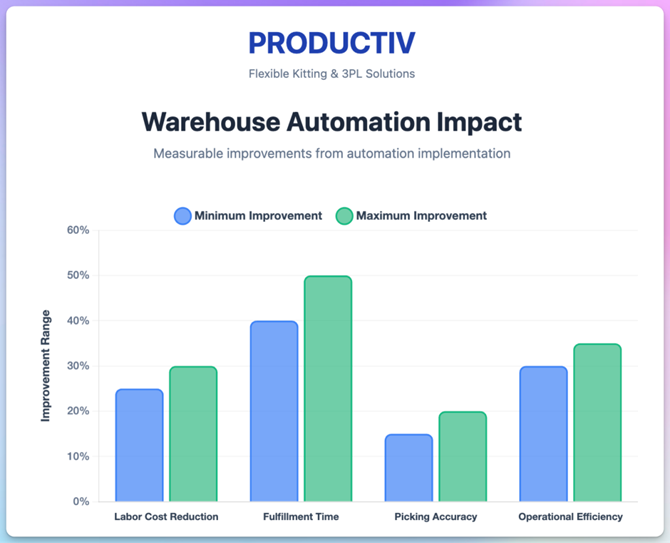
Poor warehouse organization contributes to inefficiency and errors. A well-organized facility can improve picking productivity and reduce labor costs by 20-30%.
5. Standardize Labeling and Identification Systems
Consistent labeling is fundamental to inventory accuracy; every location, pallet, box, and individual item should have a unique, scannable identifier.
To maintain proper labeling, follow these best practices:
- Implement barcode or RFID systems. Automation reduces manual entry errors and speeds up data capture.
- Use standardized label formats. Include SKU, description, quantity, lot number, expiration date, and location.
- Label at the item and case level. Provide flexibility for different pick types (case picks vs. each pick).
- Maintain label quality. Replace damaged or faded labels immediately to prevent scan failures.
- Train staff on labeling protocols. Ensure everyone follows the same standards.
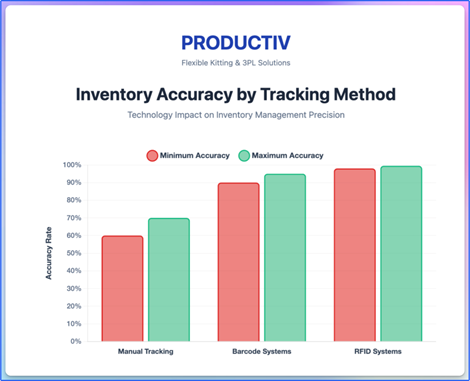
The RFID market in the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing significant growth due to increased adoption in inventory management. RFID technology enables non-line-of-sight reads and eliminates human counting errors, further improving accuracy.
6. Establish Safety Stock Levels and Reorder Points
Setting appropriate safety stock prevents stockouts during demand spikes or supply chain disruptions, while reorder points ensure timely replenishment.
Here’s how to calculate these key inventory metrics:
- Calculating reorder points. Reorder Point = (Average Daily Usage × Lead Time in Days) + Safety Stock
- Determining safety stock. Safety Stock = (Maximum Daily Usage × Maximum Lead Time) - (Average Daily Usage × Average Lead Time)
Research indicates that addressing overstocking and understocking can help businesses achieve a 10% reduction in inventory costs. The average business holds $142,000 in excess inventory beyond what's required to meet demand.
For effective implementation, consider the following approach:
- Analyze historical sales data to identify demand patterns.
- Factor in suppliers' lead-time variability.
- Consider seasonal fluctuations and promotional activities.
- Review and adjust safety stock levels quarterly.
- Use predictive analytics to improve forecasting accuracy.
Businesses that have invested in machine learning for demand forecasting achieve 90% accuracy with a 3-month lag, compared to 60% with manual forecasting.
7. Conduct Regular Physical Audits
While cycle counting handles day-to-day accuracy, annual or biannual physical inventories provide a comprehensive snapshot and help validate your perpetual inventory records.
A successful physical audit depends on following these key practices:
- Schedule during slow periods or facility closures to minimize disruption.
- Use a "blind count" method where counters don't see the expected quantities.
- Assign teams to specific zones or categories.
- Reconcile discrepancies immediately and investigate root causes.
- Document findings and implement corrective actions.
Research shows that inventory accuracy in U.S. retail operations averages only 63%. Regular physical audits combined with cycle counting help close this accuracy gap.
8. Implement Demand Forecasting and Planning
Accurate demand forecasting prevents both stockouts and excess inventory. Advanced WMS platforms offer predictive analytics and demand planning features that analyze historical data, seasonality, and market trends.
Key strategies for effective forecasting include:
- Historical analysis. Review past sales patterns to predict future demand.
- Seasonal adjustments. Account for holidays, weather, and industry-specific cycles.
- Promotional planning. Factor in marketing campaigns that will drive demand spikes.
- Collaborative forecasting. Work with sales, marketing, and suppliers to gather intelligence.
- Continuous monitoring. Update forecasts regularly based on actual performance.
Approximately 36% of supply chain professionals are actively optimizing inventory management to balance supply and demand. Meanwhile, 72% of retailers plan to reinvent their supply chain with real-time visibility enabled by automation, sensors, and analytics.
9. Train and Empower Warehouse Staff
Your team is the backbone of inventory accuracy. Well-trained employees make fewer errors, work more efficiently, and take ownership of inventory integrity.
To build a skilled, reliable warehouse team, make sure your training covers the following areas:
- System training. Ensure all staff can confidently use WMS, scanners, and other technology.
- Process documentation. Create clear SOPs for receiving, putaway, picking, and cycle counting.
- Error prevention techniques. Teach double-checking methods and verification procedures.
- Cross-training. Develop versatile employees who can work in multiple areas.
- Continuous feedback. Hold regular meetings to address challenges and share best practices.
Invest in motivational strategies that emphasize accuracy and reward high performance. When employees understand how their work impacts the bottom line, they're more engaged and careful.
10. Monitor and Analyze Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
You can't improve what you don't measure. Tracking inventory KPIs provides visibility into performance and highlights areas for improvement.
The most important inventory KPIs to monitor are:
- Inventory accuracy rate. (Counted inventory / System inventory) × 100.
- Inventory turnover ratio. Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventory Value.
- Order accuracy rate. Number of accurate orders / Total orders shipped.
- Carrying a cast of inventory. Total cost to hold inventory / Total inventory value.
- Stockout rate. Number of stockouts / Total number of orders.
Fill rate. Orders fulfilled completely from available stock / Total orders.
The average inventory turnover rate across sectors in 2024 is 8.5, though this varies significantly by industry. The Financial sector has the highest turnover at 227.67, while Capital Goods averages only 2.67.
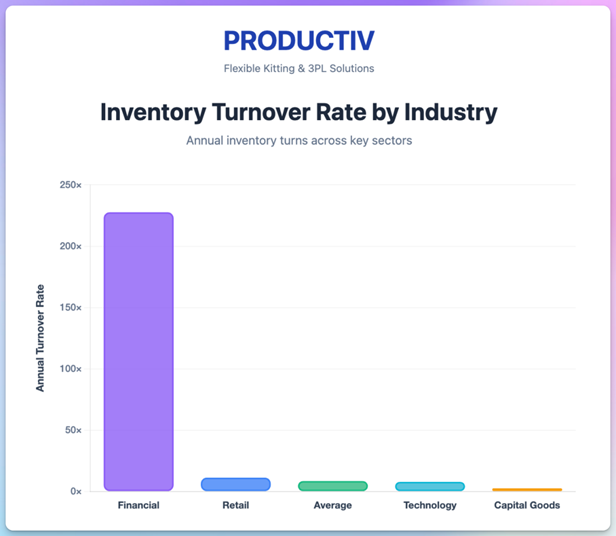
Create dashboards that display these metrics in real-time and review them during weekly management meetings. Use trends to identify problems before they escalate.
11. Invest in Automation and Robotics
Warehouse automation is transforming inventory management, with the market expected to grow from $24.09 billion in 2025 to $42.25 billion by 2029. By 2025, approximately 4.3 million commercial warehouse robots will be installed worldwide.
Key automation technologies include:
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs). Follow fixed paths using magnetic strips or wires for material transport.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs). Navigate dynamically using sensors and smart technology without fixed routes.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS). Computer-controlled systems for automatically placing and retrieving loads.
- Collaborative robots (cobots). Work alongside humans to handle physical tasks like heavy lifting, sorting, and packaging.
- Automated picking systems. Technology-assisted picking that increases speed and accuracy.
Automation reduces labor costs by 25-30% and improves key warehouse efficiency metrics, including fulfillment time, picking accuracy, and inventory management. By 2025, up to 50,000 robotic warehouses may be operational globally.
For a smooth and cost-effective rollout, keep these implementation considerations in mind:
- Start with high-impact, high-volume processes.
- Calculate ROI before investing in expensive automation.
- Ensure automation integrates with existing WMS and systems.
- Train staff to work alongside automated equipment.
- Plan for scalability as your operation grows.
Key Takeaways
Effective warehouse inventory management requires a combination of proven processes, modern technology, and engaged staff.
By implementing these 11 tips, you'll improve accuracy, reduce costs, and position your operation for sustainable growth:
- Maintain accuracy by continuously cycle-counting rather than relying solely on annual physical inventories.
- Choose the right inventory flow method (FIFO, LIFO, or FEFO) based on your product characteristics.
- Invest in WMS technology to automate tracking and gain real-time visibility.
- Optimize warehouse layout to reduce travel time and increase picking efficiency.
- Standardize labeling systems using barcodes or RFID for error-free identification.
- Set appropriate safety stock and reorder points to prevent stockouts without overstocking.
- Leverage demand forecasting to align inventory with actual customer demand.
- Train and empower staff to take ownership of inventory accuracy.
- Monitor KPIs consistently to identify trends and drive continuous improvement.
- Consider automation to reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency.
FAQ
1. What is the most accurate inventory counting method?
Cycle counting combined with ABC analysis is the most accurate approach for ongoing inventory management. This method allows you to count high-value items more frequently while maintaining overall accuracy above 95%. When paired with barcode or RFID technology, cycle counting virtually eliminates human counting errors and provides continuous validation of inventory records without disrupting operations.
2. How often should warehouses conduct physical inventory counts?
Most warehouses should conduct comprehensive physical inventories once or twice annually, supplemented by daily or weekly cycle counts. High-value A-class items should be cycle counted every 30 days, medium-value B-class items every 60 days, and low-value C-class items every 90-180 days. This combination ensures continuous accuracy while minimizing operational disruption.
3. What's the difference between FIFO and LIFO inventory methods?
FIFO (First In, First Out) ships the oldest inventory first and is essential for perishable goods, while LIFO (Last In, First Out) ships the newest inventory first and works for non-perishable items. 55% of companies use FIFO, and both GAAP and IFRS accept it. Only 15% of companies use LIFO; on the other hand, IFRS doesn’t permit it, though it can offer tax advantages during inflationary periods.
4. How can I reduce inventory holding costs?
Reduce holding costs by optimizing safety stock levels, improving demand forecasting accuracy, increasing inventory turnover through better sales and marketing alignment, implementing just-in-time inventory practices, and eliminating dead stock through regular analysis. Research shows that addressing overstocking and understocking can reduce inventory costs by 10%, while businesses with high-performing supply chains achieve revenue growth beyond industry averages.
5. What inventory accuracy rate should warehouses target?
Leading organizations target inventory accuracy rates of 98-99% or higher. While accuracy above 90% may seem reasonable, the goal should be near-perfect accuracy to prevent stockouts, reduce waste, and maintain customer satisfaction. Using automated technologies like barcode systems can achieve 90-95% accuracy, while RFID systems can reach 98-99.5%, compared to 60-70% with manual tracking methods.
6. When should I invest in warehouse automation?
Consider investing in automation when your operation experiences high labor costs, struggles with accuracy, needs to scale significantly, or faces competitive pressure to reduce fulfillment times. Start by calculating ROI on specific automation technologies for your highest-volume processes. With automation costs declining and the market growing rapidly, even mid-sized warehouses can now justify automated picking systems, AMRs, or cobots that deliver 25-30% reductions in labor costs.
7. How does a Warehouse Management System improve inventory accuracy?
A WMS improves accuracy by automating data capture through barcode or RFID scanning, eliminating manual entry errors, providing real-time inventory visibility, optimizing pick paths to reduce errors, automatically tracking inventory movement between locations, and generating automated alerts for low stock levels. Studies show that over 90% of businesses plan to automate processes using WMS by 2025, driven by the need for greater accuracy and operational efficiency.
20 Years of Kitting Excellence
Ready to Streamline Your Supply Chain?
Join industry leaders achieving 99%+ SLA performance with flexible kitting, fulfillment, and 3PL solutions.
Get in Touch